
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the joints and intervertebral discs. Osteochondrosis affects the cartilaginous tissue of the disc. As a result, the disc hardens and shrinks, losing its cushioning properties and causing severe pain.
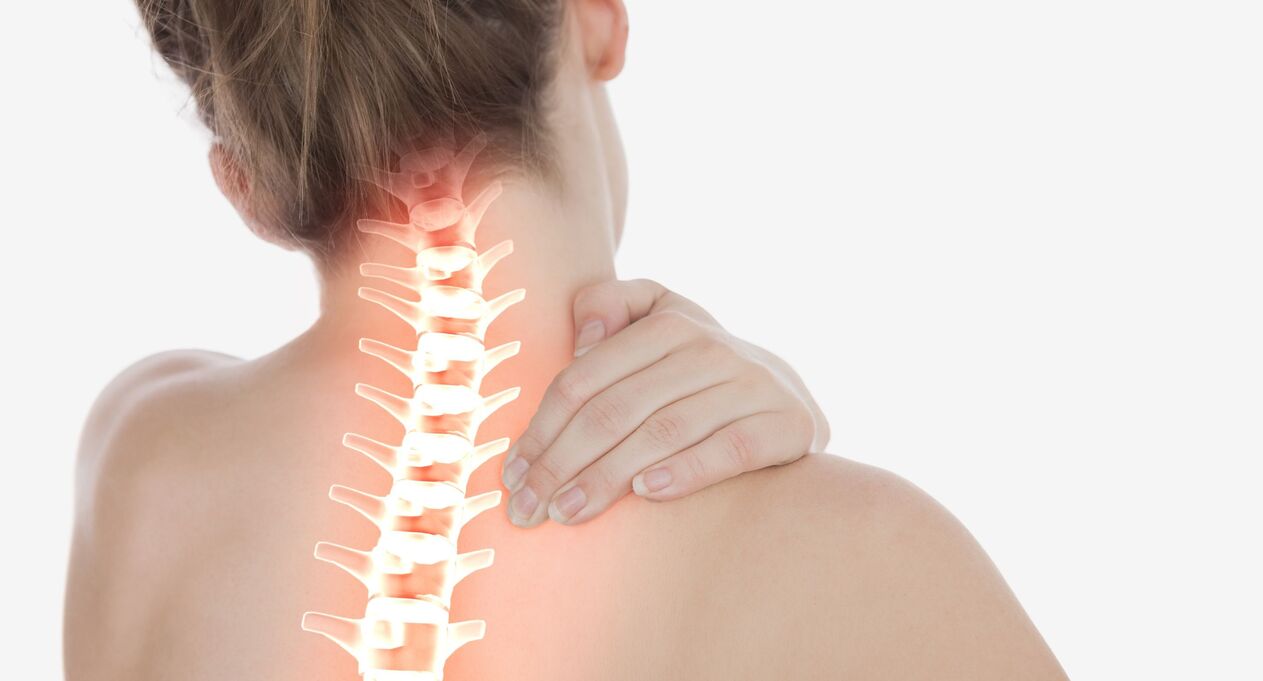
Cervical osteochondrosis is a progressive degenerative-dystrophic process that leads to deficiency, deformation and destruction of the intervertebral discs of the cervical region. Loss of shock-absorbing cartilage causes pain both due to exposure of the articular surface (spondyloarthrosis) and due to compression of the spinal nerve roots.
In the absence of timely treatment, ossification of the spine is possible with loss of natural flexibility, disruption of blood supply to the brain, deterioration of nerve conduction in the parts of the body that innervate the roots of the cervical spine.
Pathology can develop independently and as part of a general lesion of the spine, covering the thoracic, lumbar and sacral regions.
General information about cervical osteochondrosis
It is believed that osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is more common than in other departments. In fact, this is not so - the dystrophic phenomenon develops equally at all points of maximum load - in the area of the main bend of the spinal column (the lower the department is located, the greater the load it bears). However, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are more pronounced, so it seems to occur more often. This is due to the high mobility of the neck vertebrae, which at the same time hold the head, as well as the peculiarity of the location of the outlet from the root of the spinal cord.
On the note!According to statistics, this disease affects more than 60% of middle-aged and older people. However, recently there has been a rejuvenation of the pathological process - the pathology occurs in young people and even in teenagers. This is due to the general computerization of studies and work, as well as a decrease in physical activity and deterioration in the quality of nutrition.
Taking into account the age of the audience, 2 forms of cervical osteochondrosis can be distinguished - physiological and pathological.
physiological processassociated with the natural aging of the body, when the symptoms of the disease are the result of gradual wear of the intervertebral disc. This process occurs under the influence of the endocrine system and is a consequence of menopausal changes. The destruction of the cartilage structure starts from the center of the intervertebral disc and is accompanied by the gradual replacement of cartilage tissue with fibrous tissue. Pathology cannot be restored, but can be compensated with special drugs.
Pathological processassociated with abnormal destructive changes in the body - immune, dystrophic, inflammatory, metabolic. First of all, pericartilaginous tissue is involved - salt deposits appear on bone structures, nerve roots become inflamed, atrophy or hypertonicity of skeletal muscles occurs, which leads to impaired blood circulation in the head-neck-chest area. With timely diagnosis, pathology can be treated and end with the complete restoration of the function of healthy organs and tissues.
Stages of cervical osteochondrosis and their symptoms
There are 4 main stages of the pathological process:
- Stage 1 - expressed by slight discomfort and muscle tension in the diseased area, the cartilage disc loses its stability;
- Stage 2 - there is localized pain, especially when moving the head. The intervertebral disc is deformed, the fibrous ring begins to collapse, the distance between the vertebrae decreases;
- Stage 3 - pain increases and becomes constant, movement is limited. Turning the head can trigger an attack of dizziness, nausea, impaired blood supply to the brain leads to general lethargy, fatigue, impaired concentration, cartilage becomes thinner, vertebrae are close, fibrous rings are completely destroyed with the risk of intervertebral hernia;
- 4th stage - the pain syndrome completely paralyzes the neck area; cerebral blood circulation is impaired and requires constant medical support; vertebrae begin to grow together.
Cervical osteochondrosis: signs, symptoms, pathological treatment
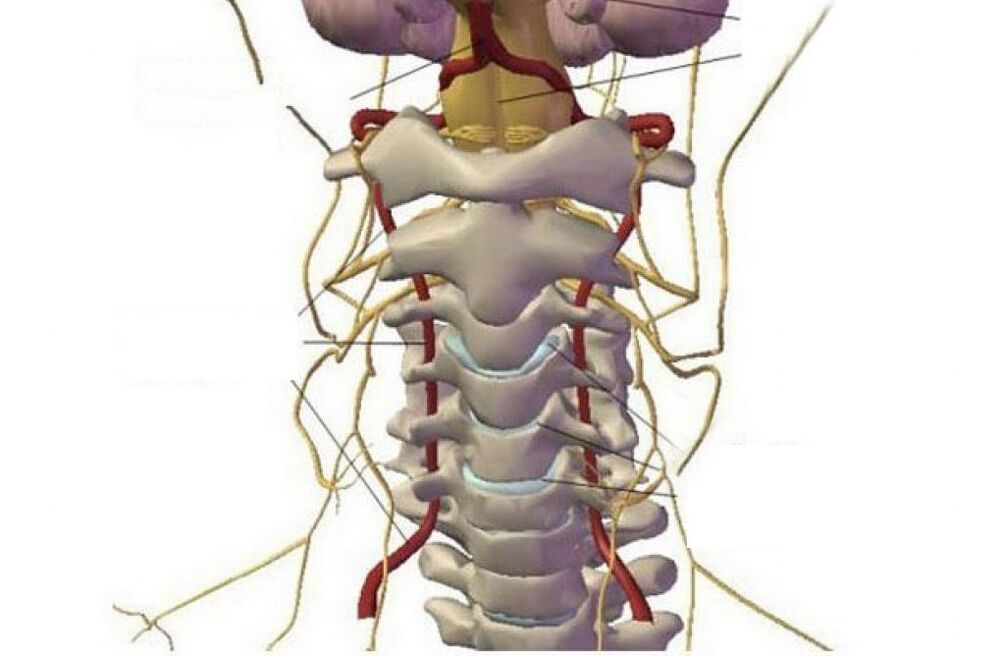
In the first stage, osteochondrosis is asymptomatic. As the disease progresses, a distinctive feature becomes the presence of painful or uncomfortable sensations in the head, neck and chest, less often in the upper limbs.
All possible symptoms can be conditionally attributed to 4 types of syndromes: heart, vertebral, radicular (nerve) and vertebral artery syndrome (with circulatory disorders).
Vertebral Syndrome:
- irritation in the neck when turning / tilting the head;
- when the disease progresses, pain and difficulty in movement occur;
- morphological structural disorder in the vertebral body and intervertebral space (visible on x-ray).
Heart Syndrome:
- shortness of breath, weakness;
- feeling of incomplete inspiration, lack of air;
- spontaneous phenomena of the cardiovascular system - angina pectoris, retrosternal pain, burning;
radicular syndrome:
- numbness of the tongue, shoulders, fingers, occipital region;
- difficulty swallowing;
- discomfort in the area between the shoulder blades;
- headache in the occiput and forehead.
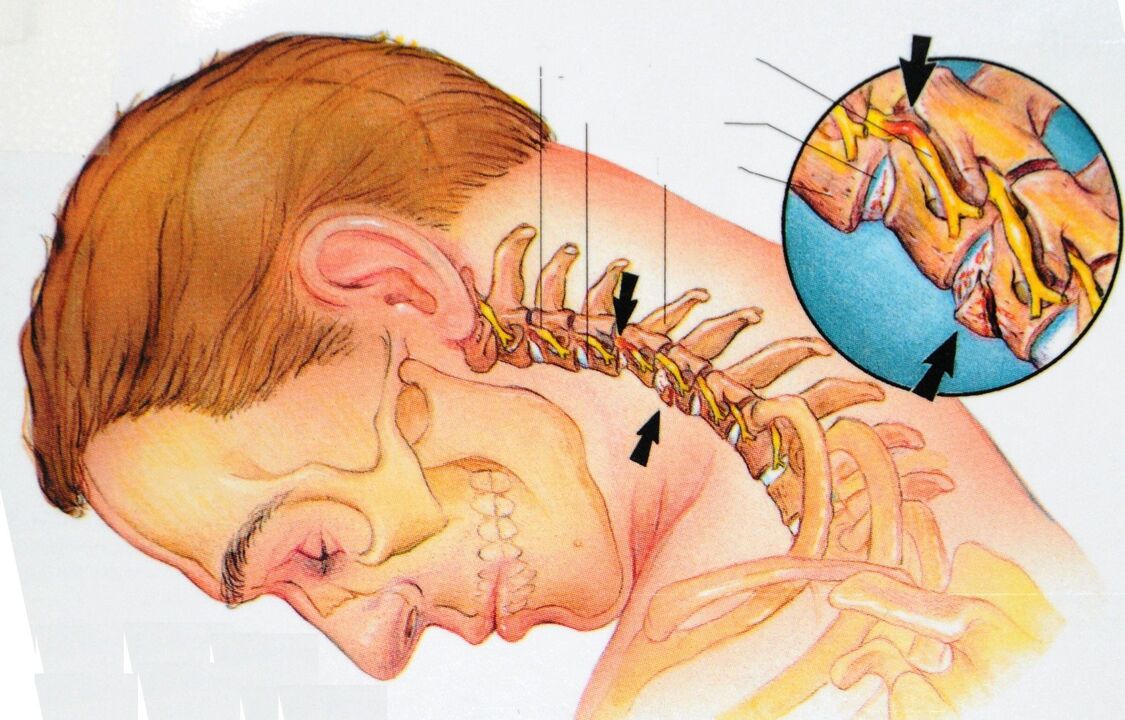
vertebral artery syndrome:
- unreasonable jumps in blood pressure;
- dizziness, until loss of consciousness;
- tinnitus, the feeling of cotton wool in the head;
- temporary blindness, "fly" in the eye;
- periodic nausea, especially when moving the head;
- headache - especially in the back of the head, as well as migraine;
- drowsiness, decreased performance, memory, concentration, depression.
Attention!All these syndromes must be combined with each other. The absence of symptoms of one of them may be the reason for differential diagnosis with other groups of diseases.
Causes of cervical osteochondrosis
Dystrophic phenomena in the region of the cervical spine are associated with the vertical position of the skeleton and the specific distribution of static and dynamic loads, which largely depends on the current posture and the level of skeletal muscle development.
- lack of movement - what does not develop - deteriorates: muscles weaken, tissues are destroyed;
- incorrect static posture - muscle clamps lead to circulatory disorders with subsequent tissue degeneration;
- lack of nutrition or an unbalanced diet - the body must receive everything it needs for the construction and renewal of the bone and cartilage structure of the skeleton, maintaining muscle tone;
- obesity, overweight, carrying heavy loads - the load on the skeletal structure increases;
- constant nervous tension and nervous stress;
- hypothermia of the cervical region - "cold", "bloated" - provokes a hidden inflammatory process;
- the presence of autoimmune diseases involving cartilage leading to premature destruction;
- endocrine pathology disrupts mineral metabolism, reduces the absorption of calcium, silicon, phosphorus and other elements of bone and cartilage tissue;
- neck injury;
- congenital anomalies of the spine and adjacent muscles.
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis
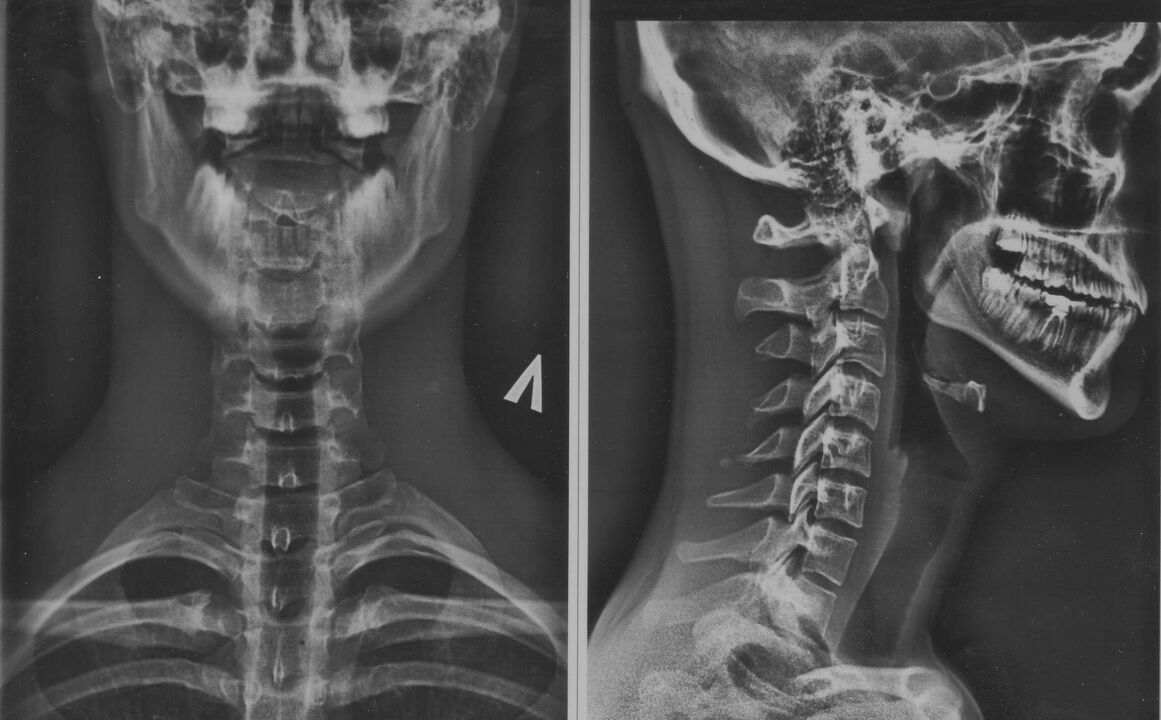
The diagnosis of "osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae" is made difficult by the low specificity of the symptoms and the wide variety of its manifestations. During the examination, you need to consult with a neurologist, surgeon, orthopedist, cardiologist.
A physical examination is conducted by the doctor by questioning the patient. The main diagnostic burden lies in instrumental and laboratory research methods.
- radiography of the cervical region; at the initial stage of the process, MRI of the cervical region will be more informative - it will provide high-quality visualization of hard and soft tissues - it will show the condition of the intervertebral disc, the presence of osteophytes, defects, damage to nerve roots and blood vessels; assess the condition of ligaments, muscles, bone tissue; shows the dynamic state of soft tissue;
- dopplerography of the neck canal will help assess hemodynamics and the degree of damage to the blood vessels (in particular, the condition of the vertebral arteries);
- contrast myelography - will help with suspected violations of nerve processes;
- ECG and cardiac echocardiography are used in the differential diagnosis of cardiac syndromes with cardiovascular diseases.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis
A complex of therapeutic measures is formed taking into account the stage of the disease (acute, chronic), the level of damage and the cause of the pathology. Use conservative treatment, surgery, mixed approach.
conservative effect
It is a gradual recovery or compensation of damage against the background of symptomatic treatment. Including drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage methods.
Medical treatment:
- pain relievers - especially topical gels and ointments; in severe cases - general painkillers in the form of tablets;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs, as well as corticosteroids (short course if necessary);
- drugs to improve microcirculation and blood circulation in general;
- chondroprotectors - means to protect and restore cartilage tissue;
- muscle relaxants - to eliminate clamps and muscle spasms;
- vitamin and micro complex - necessary for nutrition and tissue support with building elements.
When the acute symptoms subside, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and self-massage methods are connected.
Physiotherapyimprove the nutrition of cartilage and bone tissue. due to the restoration of blood supply in the damaged area. To avoid complications, it is recommended to use the method of isometric movements, when instead of real rotation and tilting of the head, which can cause damage, their imitation is used.
Attention!All actions should be taken only after diagnosis and consultation with a doctor.
This technique allows you to develop and strengthen the atrophied short muscles of the neck and stabilize the position of the cervical spine. Basic training sequence:
- Place your right palm on the side of the head - for 10 seconds, press your palm on the head, while tensing the muscles of the head and neck for resistance - the head should remain motionless.
- Lower your hands, relax the head and neck muscles as much as possible for 20 seconds.
- Repeat the exercise with your left hand.
- Put both hands on your forehead with your palms - for 10 seconds, press on your forehead, as if trying to tilt your head back, while tensing your neck muscles to resist the movement. The head must remain motionless.
- Lower your arms, relax your muscles as much as possible, just like the previous exercise.
- Place both palms on the area above the back of the head. By analogy, perform a pressure load on the neck muscles, try to tilt your head forward - it should still not move.
- Lower your arms, relax your neck and head muscles. Repeat the exercise set 4-10 times.
After strengthening the short muscles of the neck, you can start doing dynamic exercises.
On the note!Swimming and water gymnastics have proven themselves as techniques to restore cervical mobility.
Self massageallows you to reduce the intensity of local reactions and relieve muscle cramps during static work. Implementation rules:
- area of influence - the back of the head, back and side surfaces of the neck;
- perform the procedure in a sitting position;
- movement should be done in the direction from the spine;
- use only fingertips;
- avoid pressure on the inflamed area;
- perform movements smoothly - sharp pressure can be dangerous.
Physiotherapytypical for inpatient treatment and spa rehabilitation. Well proven:
- electrophoresis - heats the area, improves microcirculation, is used for deeper penetration of topical preparations;
- magnetotherapy;
- amplipulse;
- UHF.
Surgical intervention is indicated for complicated extrusion, spinal cord injury and intractable pain syndrome.
Is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous
The neck area concentrates a dense intertwining of the main blood vessels, nerve processes and the dynamic structure of the bone skeleton. In the absence of treatment, serious pathological changes can be observed:
- the weakness of the fibrous ring creates dislocations and subluxations in the most mobile areas of the vertebrae;
- the presence of osteophytes and muscle spasms leads to violation of nerve roots and blood vessels with the formation of compression syndrome;
- The destruction of the cartilaginous disc and convergence of the vertebrae leads to intervertebral hernia with violation of nerve tissue.
Each of these phenomena is followed by a clear negative reaction from the whole organism.
Possible complications and consequences
The list of the most common complications of cervical osteochondrosis includes:
- vegetovascular dystonia;
- hypertension;
- oxygen starvation of the brain and its structure;
- retinal dystrophy of the eye with visual impairment;
- damage to the thyroid gland;
- dysfunction of the esophagus and trachea - difficulty swallowing and respiratory spasms;
- uncontrollable pain in the head, neck, chest, upper limbs;
- convulsions and numbness of the face, hands;
- disorders of the hypothalamus-pituitary system, which involves the failure of the entire body's hormonal activity.
Preventive measures of cervical osteochondrosis
The most effective treatment is disease prevention. Prevention will help you with this. It is enough to follow some basic recommendations:
- correct your posture,
- creating a comfortable workplace;
- during sedentary work, take a break for "physical education minutes";
- include in your diet foods rich in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, silicon - fish, nuts, seeds, legumes, dairy products, fresh vegetables, fruits; limit intake of salty, sweet, starchy and spicy foods;
- for sleep and rest, use orthopedic mattresses and pillows;
- go for non-strength sports - it is better to give preference to swimming.
Although you cannot take into account all the needs, moderate exercise, proper nutrition and attention to your posture can significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology.
The hidden cause of impotence, male and female infertility is osteochondrosis
Even at school, in biology lessons, they try to convey important information about the great role of the spine in maintaining human health. Unfortunately, many at that time were involved in more important matters and did not listen to the teacher's words. But in vain! Doctors say that disorders of the musculoskeletal system, in particular, caused by osteochondrosis, can cause the development of a large number of various serious diseases.
Why osteochondrosis has a strong destructive effect on the human body
Often men experience impotence and infertility, and women try in vain to get pregnant and do not suspect that this can be caused by ordinary osteochondrosis. The fact is that the cause of the development of the disease lies in the violation of the blood supply to the vertebral tissue and the muscles that surround it. Since there are no blood vessels in the intervertebral discs, they are the first to experience a lack of water and various other substances. This leads to a fracture of the cartilage, which means that the disc can no longer absorb the load on the spine. This is where the constant back pain comes in.
If at this stage you do not intervene in the process, then osteochondrosis will continue to develop and give complications, for example, a herniated disc. This, in turn, causes a violation in the apparatus of the spinal cord segment and affects blood circulation, including in the pelvic organs. This is the main reason for the development of many disorders in the work of internal organs, as well as impotence and infertility that interest us.
The development of impotence in men, in addition to violations at the physical level, also contributes to psychological factors. After all, for every normal and full man, even a single failure in bed becomes a drama, and it does not matter if it is caused by an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, sciatica, or other sources of back pain.
Men may begin to experience difficulty with erections in the presence of cervical or lumbar degenerative disc disease. But in each case, the pathology develops according to its own mechanism.
Cervical osteochondrosis
With the presence of this type of disease, there is a decrease in the quality of blood circulation in the brain, which causes damage to the production of sex hormones and substances responsible for vascular tone. Therefore, with cervical osteochondrosis, often patients complain of decreased sexual desire, anorgasmia, and problems with ejaculation.
Lumbar osteochondrosis
Since the pelvic area, which is where the male genital organs are located, is, as it were, in a state of "turning off" due to disruption of the spinal cord, nerve impulses cannot always penetrate the genitals, which leads to erectile dysfunction.
Female and male infertility due to osteochondrosis
Often, in the absence of other prerequisites, unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child in men and women may be the result of pathological processes accompanying osteochondrosis. Often, the cause of the problem does not lie in a violation of the blood supply to the organs located in the small pelvis, but in a neurological disorder.
Examination of women with infertility shows degenerative changes in the lower thoracic spine and lower back. In infertile men, osteochondrosis affects the lumbosacral region. Such differences in the areas affected by osteochondrosis are explained by the peculiarities of the structure and preservation of pelvic organs in representatives of different sexes.
Sometimes women cannot get pregnant even if they do not experience any signs of illness and do not feel the slightest discomfort in the back. This is mainly due to the fact that disorders in the reproductive system can occur even if only the anterior root of the spinal cord is damaged, which is not accompanied by pain.
Therefore, everyone who suffers from sexual and reproductive dysfunction is highly recommended to undergo the most complete physical examination, not forgetting the neuropathologist and the vertebrologist. It is possible that the root of the problem lies precisely in the pathology of the spine.
































